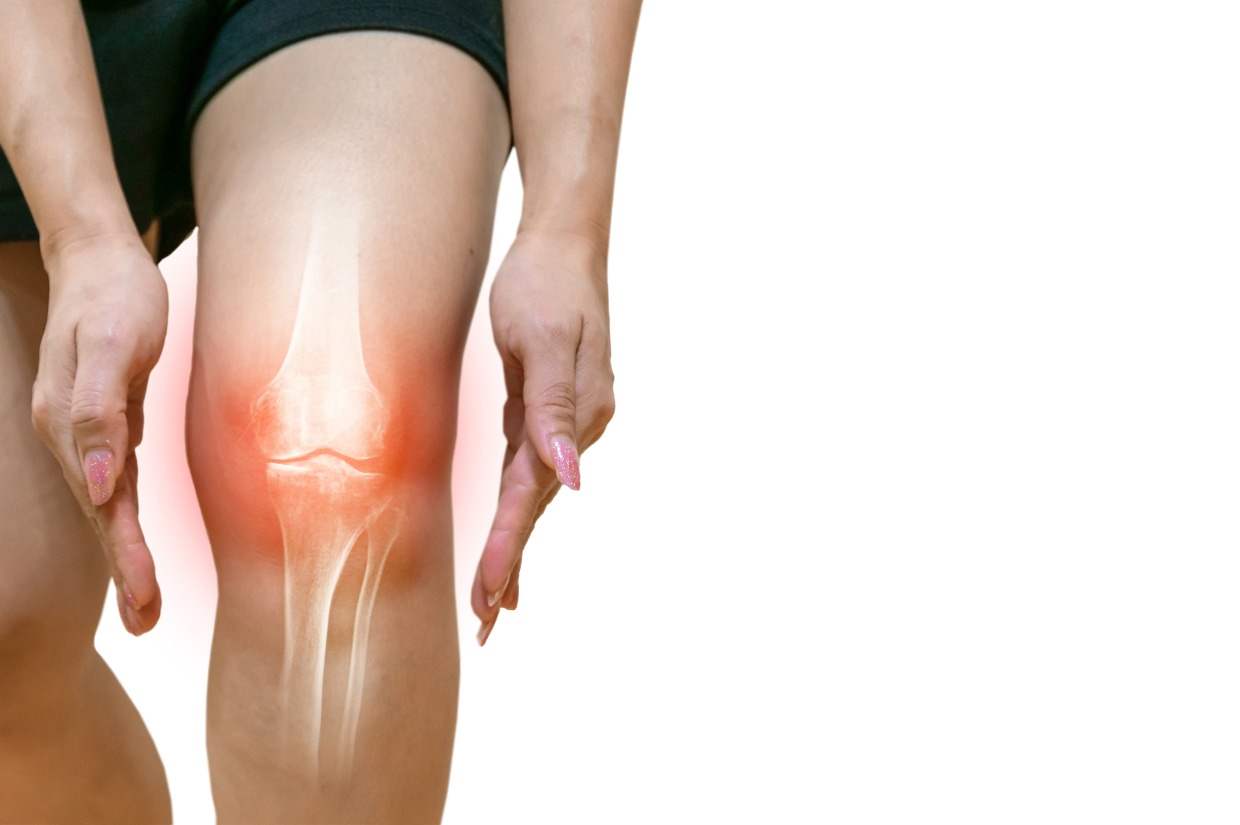
Osteoarthritis in knee is a prevalent and debilitating condition characterized by the gradual breakdown of cartilage and the underlying bone within the knee joint. This degenerative joint disease affects millions of people worldwide, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Osteoarthritis often develops gradually over time, primarily affecting older adults, although it can also occur as a result of injury or overuse of the knee joint. The onset of osteoarthritis is typically marked by symptoms such as joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and decreased range of motion, which can significantly impact an individual’s ability to perform daily activities and maintain an active lifestyle.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies for osteoarthritis in the knee is crucial for reclaiming mobility and improving overall quality of life. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore five effective strategies to manage osteoarthritis in knee, empowering individuals to take control of their condition and achieve optimal joint health.
1. Maintain a Healthy Weight to Alleviate Joint Stress
Excess weight places significant stress on the knee joints, exacerbating symptoms of osteoarthritis and accelerating joint degeneration. Individuals with osteoarthritis in knee can benefit greatly from weight management strategies aimed at reducing joint strain. By adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise and a balanced diet, individuals can achieve and maintain a healthy weight, thereby alleviating pressure on the knee joints and reducing pain and discomfort.
2. Engage in Low-Impact Exercises to Improve Joint Function
Regular physical activity is essential for managing osteoarthritis in knee. Low-impact exercises, such as walking, swimming, cycling, and tai chi, help strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee joint, improve flexibility, and enhance joint stability. These exercises promote joint lubrication, reduce stiffness, and increase range of motion, allowing individuals to maintain mobility and functionality despite the challenges posed by osteoarthritis.
3. Utilize Assistive Devices for Support and Stability
Assistive devices, such as knee braces, orthotic inserts, and walking aids, can provide valuable support and stability to individuals with osteoarthritis in knee. These devices help distribute weight evenly, reduce joint pressure, and alleviate discomfort during weight-bearing activities. Customized orthotics can correct alignment issues and improve gait mechanics, reducing the risk of further joint damage and enhancing overall mobility.
4. Explore Non-Surgical Treatment Options for Pain Management
Non-surgical treatment modalities offer effective pain relief and symptom management for osteoarthritis in knee. These options may include:
Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can help alleviate pain and inflammation associated with osteoarthritis. In more severe cases, corticosteroid injections may be administered to provide temporary relief from pain and swelling.
Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises, manual therapy techniques, and therapeutic modalities prescribed by a physical therapist can improve joint function, reduce pain, and enhance mobility in individuals with osteoarthritis.
Joint Injections: Hyaluronic acid injections, also known as viscosupplementation, may be recommended to lubricate the joint and provide cushioning, thereby relieving pain and improving joint mobility.
5. Consider Surgical Intervention for Advanced Osteoarthritis
In cases where conservative treatments fail to provide adequate relief, surgical intervention may be necessary to address advanced osteoarthritis in knee. Common surgical procedures for osteoarthritis may include:
Total Knee Replacement (TKR): TKR surgery involves replacing damaged knee joint surfaces with artificial implants, restoring joint function and relieving pain.
Partial Knee Replacement: In select cases, partial knee replacement may be performed to replace only the damaged portion of the knee joint, preserving healthy tissue and facilitating a quicker recovery.
Osteotomy: Osteotomy involves realigning the bones around the knee joint to redistribute weight and alleviate pressure on damaged areas, delaying or preventing the need for joint replacement surgery.
Conclusion: Empowering Individuals to Manage Osteoarthritis in Knee
Osteoarthritis in knee is a chronic and progressive condition that requires comprehensive management strategies to alleviate symptoms and maintain mobility. By implementing lifestyle modifications, engaging in appropriate exercises, utilizing assistive devices, exploring non-surgical treatments, and considering surgical options, when necessary, individuals can effectively manage osteoarthritis and reclaim their quality of life.
It is essential for individuals with osteoarthritis in knee to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to their specific needs and preferences. With the right approach and support, individuals can overcome the challenges of osteoarthritis and enjoy an active and fulfilling life. Remember, proactive management and a positive outlook are key to managing osteoarthritis in knee and preserving joint health for years to come. By empowering individuals with knowledge and resources, we can help them navigate their osteoarthritis journey with confidence and resilience.
Visit Dr. Dhaiwat Shukla, the best Rheumatologist in Ahmedabad known for his compassionate approach to rheumatological care. His expertise, personalized treatment plans, and commitment to improving patients’ well-being make him a trusted choice for those seeking relief from rheumatic conditions.