Scleroderma, a chronic autoimmune disease, affects connective tissues in the body, leading to skin thickening and hardening. The name “scleroderma” is derived from the Greek words “sclero,” meaning hard, and “derma,” meaning skin. Recognizing the early scleroderma signs is crucial for timely diagnosis and management of this condition. In this blog, we will delve into the various symptoms and early warning signs of scleroderma, helping you understand how to identify this complex disease.
Understanding Scleroderma
Scleroderma is characterized by an overproduction of collagen, a protein that helps in the formation of connective tissues. This overproduction causes the skin and other organs to harden and function abnormally. There are two main types of scleroderma: localized and systemic. Localized scleroderma primarily affects the skin, while systemic scleroderma (also known as systemic sclerosis) can impact internal organs and blood vessels as well.
Early Scleroderma Signs
Early detection of scleroderma signs can significantly improve the management and prognosis of the disease. Here are some common early signs to watch for:
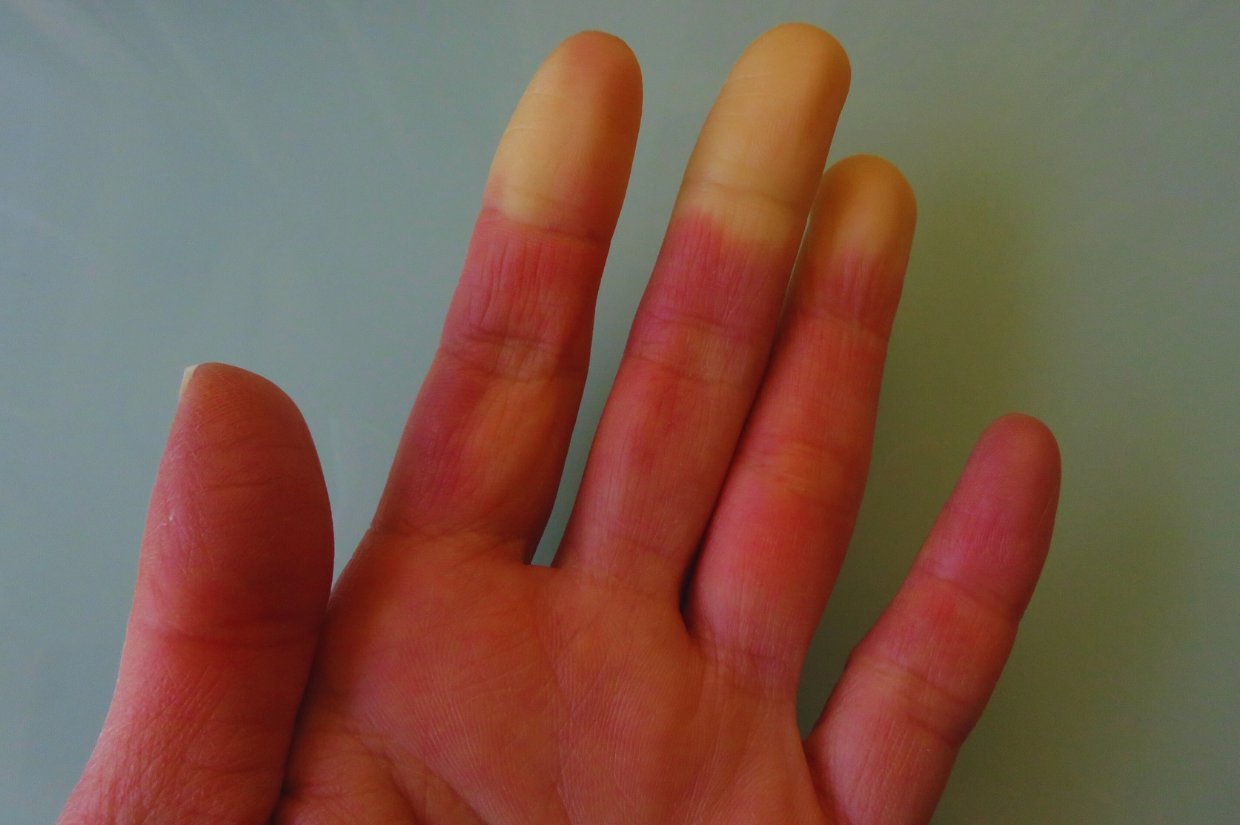
1. Raynaud’s Phenomenon
One of the most common early scleroderma signs is Raynaud’s phenomenon. This condition causes the blood vessels in the fingers and toes to constrict in response to cold temperatures or emotional stress, leading to color changes in the skin. The affected areas typically turn white, then blue, and finally red as blood flow returns. This can be accompanied by numbness, tingling, and pain.
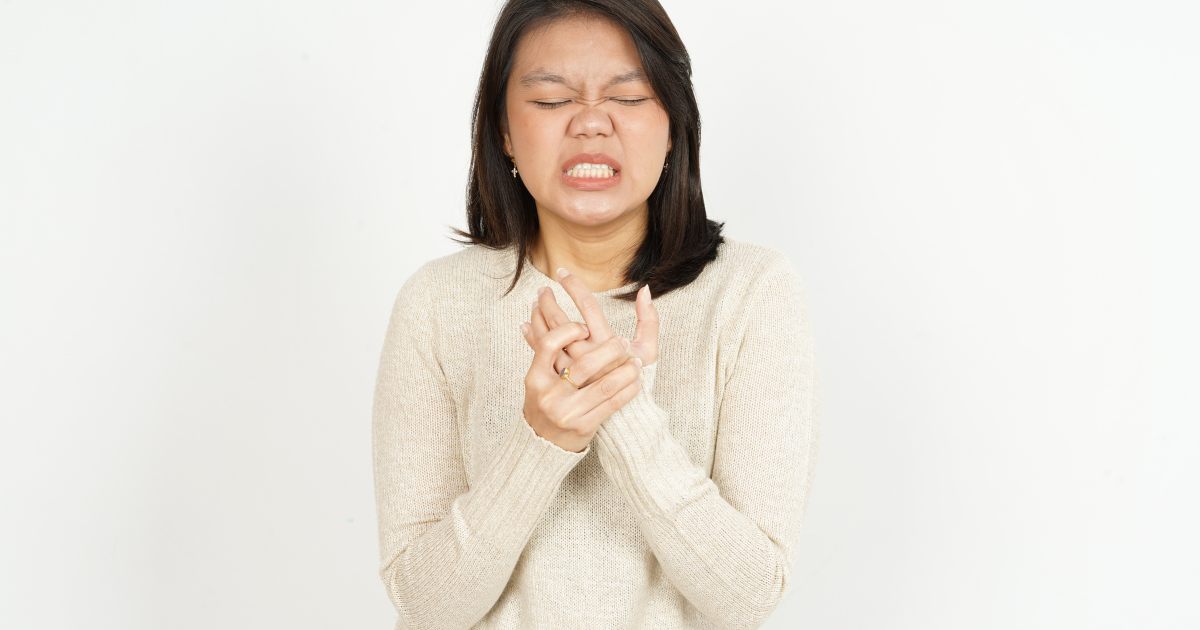
2. Skin Changes
Scleroderma often begins with changes in the skin. Early scleroderma signs include swelling, puffiness, and tightness of the skin, particularly in the fingers and hands. As the disease progresses, the skin may become thickened, shiny, and hard. These changes can make it difficult to move the affected joints.
3. Swollen Fingers or Hands
Swelling of the fingers or hands, especially in the morning, is another early scleroderma sign. This swelling can be accompanied by stiffness and a feeling of tightness in the skin.
4. Fatigue
Persistent fatigue is a common symptom among those with scleroderma. This fatigue can be severe and debilitating, impacting daily activities and overall quality of life.
5. Gastrointestinal Issues
Early scleroderma signs can also include gastrointestinal problems such as acid reflux, difficulty swallowing, bloating, and constipation. These symptoms arise due to the hardening of connective tissues in the digestive tract, which affects its normal function.
6. Joint Pain and Stiffness
Joint pain and stiffness are frequent early scleroderma signs. The tightening of the skin around the joints can lead to decreased flexibility and mobility, causing discomfort and pain.
7. Heartburn and Digestive Issues
Persistent heartburn and digestive problems, like bloating and difficulty swallowing, can be early indicators of scleroderma. These issues occur because the disease can cause the esophagus and other parts of the digestive system to harden and function abnormally.
8. Shortness of Breath
As scleroderma progresses, it can affect the lungs, leading to shortness of breath and a persistent cough. These respiratory issues are significant scleroderma signs and should not be ignored.
9. Hair Loss
Localized hair loss can occur in areas where the skin has thickened and hardened. This is another scleroderma sign that might appear early in the disease.
Recognizing Systemic Scleroderma Signs
Systemic scleroderma, or systemic sclerosis, can affect multiple organ systems. Recognizing the signs of this more severe form is critical for early intervention and management.
1. Pulmonary Issues
Systemic scleroderma can lead to pulmonary hypertension (high blood pressure in the lungs) and interstitial lung disease (scarring of lung tissue). Symptoms include shortness of breath, a persistent dry cough, and fatigue.
2. Renal Involvement
Kidney involvement in systemic scleroderma can lead to scleroderma renal crisis, characterized by sudden onset high blood pressure and rapid kidney failure. This is a medical emergency and requires immediate attention.
3. Cardiovascular Symptoms
Cardiovascular issues, such as irregular heartbeats, pericarditis (inflammation of the sac surrounding the heart), and congestive heart failure, can also be scleroderma signs. These symptoms warrant immediate medical evaluation.
4. Musculoskeletal Problems
In addition to joint pain and stiffness, systemic scleroderma can cause muscle weakness and atrophy. These musculoskeletal issues can significantly impact mobility and daily functioning.
5. Digestive System Complications
Systemic scleroderma can cause severe digestive issues, including malabsorption, weight loss, and gastrointestinal bleeding. These symptoms result from the hardening of the tissues in the digestive tract, affecting its ability to process food properly.
Importance of Early Detection
Recognizing early scleroderma signs is vital for several reasons:
- Early Diagnosis: Early detection allows for prompt diagnosis, which is crucial for managing symptoms and preventing complications.
- Treatment Initiation: Early intervention can slow disease progression and improve quality of life. Medications and therapies can be more effective when started early.
- Monitoring and Management: Regular monitoring and management of the disease can help prevent severe complications, particularly those affecting internal organs.
- Support and Education: Early diagnosis provides an opportunity for patients to educate themselves about the disease and seek support from healthcare providers and support groups.
Seeking Medical Advice
If you notice any early scleroderma signs, it is essential to seek medical advice promptly. Here are some steps to take:
- Consult a Rheumatologist: A rheumatologist specializes in autoimmune diseases and can provide a comprehensive evaluation and diagnosis.
- Document Symptoms: Keep a record of your symptoms, including when they started, their frequency, and any factors that seem to worsen them. This information can be helpful during medical consultations.
- Undergo Diagnostic Tests: Your doctor may recommend various tests, such as blood tests, skin biopsies, and imaging studies, to confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of the disease.
- Follow a Treatment Plan: If diagnosed with scleroderma, work with your healthcare team to develop a personalized treatment plan. This plan may include medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Living with Scleroderma
While scleroderma is a chronic condition with no cure, many people live full and active lives with proper management. Here are some tips for living with scleroderma:
- Stay Active: Regular exercise can help maintain joint flexibility and muscle strength. However, it’s important to tailor your exercise routine to your abilities and consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new exercise program.
- Protect Your Skin: Use moisturizers to keep your skin hydrated and avoid harsh chemicals. Protect your skin from extreme temperatures, and take measures to prevent injuries.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: A nutritious diet can help manage digestive issues and maintain overall health. Avoid foods that trigger acid reflux and consider smaller, more frequent meals.
- Manage Stress: Stress can exacerbate symptoms, so it’s essential to find ways to relax and manage stress. Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and hobbies can be beneficial.
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with the latest research and treatments for scleroderma. Join support groups and connect with others who understand your experience.
Conclusion
Recognizing early scleroderma signs is essential for timely diagnosis and effective management of the disease. From Raynaud’s phenomenon and skin changes to gastrointestinal and respiratory issues, these symptoms can provide crucial clues for identifying scleroderma. Early detection, followed by appropriate medical care and lifestyle adjustments, can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals living with this challenging condition.
By staying informed about scleroderma signs and seeking prompt medical advice, you can take proactive steps to manage the disease and maintain your health and well-being. Remember, while scleroderma is a complex and chronic illness, with the right support and care, you can lead a fulfilling life.