Rheumatic fever is a serious inflammatory disease that can develop as a complication of untreated strep throat or scarlet fever. It mainly affects children and adolescents but can occur at any age. Many people wonder, “Is rheumatic fever communicable?” While rheumatic fever itself is not contagious, the bacterial infection that leads to it can spread from person to person. Understanding the disease, its causes, symptoms, and prevention is crucial in reducing its impact.
In this blog, we will explore what is rheumatic fever disease, its symptoms, complications, and ways to prevent it. We will also discuss whether it is a viral infection, different types of rheumatic fever, and what causes rheumatic pain.
What is Rheumatic Fever Disease?
Rheumatic fever is an autoimmune inflammatory disease that occurs as a delayed reaction to an untreated or inadequately treated Group A Streptococcus (GAS) infection, commonly known as strep throat. It can cause permanent damage to the heart, joints, skin, and nervous system if left unchecked.
The disease primarily affects children between 5 and 15 years old but can occur in adults as well. Early diagnosis and treatment of strep throat are key to preventing rheumatic fever.
Causes of Rheumatic Fever
Fever is caused by an abnormal immune response to a Group A Streptococcus (GAS) bacterial infection. When strep throat or scarlet fever is not properly treated with antibiotics, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues in the body, leading to inflammation in the heart, joints, skin, and brain.
Is Rheumatic Fever a Virus?
No, rheumatic fever is not a viral infection. It is caused by a bacterial infection (Group A Streptococcus). However, the symptoms may sometimes mimic those of viral infections, leading to confusion. Since it is not a virus, antibiotics can be effective in preventing its development by treating the initial bacterial infection.
Is Rheumatic Fever Communicable?
Rheumatic fever itself is not contagious, but the bacterial infection that triggers it strep throat is highly communicable. Strep throat spreads through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or shares utensils. If left untreated, some individuals may develop rheumatic fever.
To prevent the spread of strep throat and reduce the risk of fever, it is important to:
- Maintain good hygiene by washing hands frequently.
- Cover the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing.
- Avoid close contact with infected individuals.
- Seek medical attention for sore throats, especially in children.
- Complete the full course of antibiotics if prescribed.
Types of Rheumatic Fever
This fever does not have distinct classifications, but its effects vary based on severity and the organs affected. It primarily impacts the:
- Cardiac System (Rheumatic Heart Disease) – Inflammation of the heart valves, leading to permanent damage and heart failure if untreated.
- Joints (Arthritis-Like Symptoms) – Painful, swollen joints, often moving from one joint to another.
- Nervous System (Sydenham’s Chorea) – Uncontrollable movements, emotional instability, and behavioral changes.
- Skin (Rash and Nodules) – Erythema marginatum (red rash with a ring-like pattern) and subcutaneous nodules (small lumps under the skin).
Each patient may experience a different combination of these symptoms, making diagnosis complex.
What is Rheumatic Pain?
Rheumatic pain is the discomfort and inflammation experienced in the joints due to rheumatic fever. It usually affects larger joints like the knees, ankles, elbows, and wrists, and may shift from one joint to another. The pain is temporary but can be severe.
To manage pain:
- Anti-inflammatory medications such as aspirin or ibuprofen can help.
- Resting the affected joints can reduce strain.
- In severe cases, corticosteroids may be required.
Symptoms of Rheumatic Fever
The symptoms of fever usually appear 2 to 4 weeks after a strep throat infection. Common symptoms include:
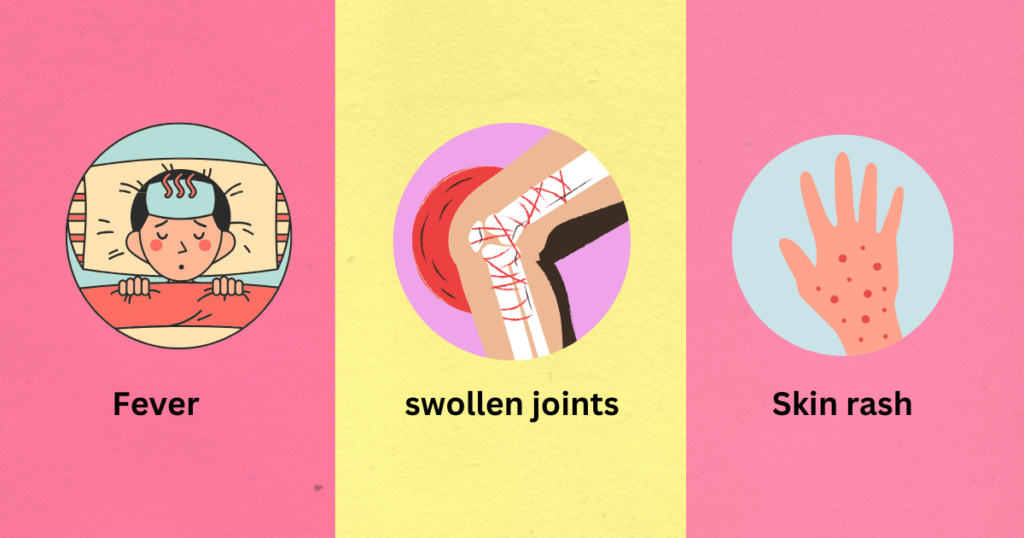
- Fever
- Painful, swollen joints (arthritis-like symptoms)
- Fatigue and weakness
- Chest pain or shortness of breath (if heart is affected)
- Skin rash (erythema marginatum)
- Uncontrolled movements (Sydenham’s chorea)
- Lumps under the skin (nodules)
If any of these symptoms occur after a sore throat, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Rheumatic Fever
Diagnosis:
Doctors diagnose fever using the Criteria, which include:
- A history of recent strep throat infection.
- Presence of major symptoms (arthritis, heart inflammation, chorea, skin rash, nodules).
- Supporting minor symptoms (fever, joint pain, abnormal blood tests).
- Confirmatory tests like throat swabs, blood tests (ASO titer), and echocardiograms.
Treatment:
There is no single cure for fever, but it can be managed through:
- Antibiotics – To eliminate Group A Streptococcus infection.
- Anti-inflammatory Medications – To reduce joint pain and inflammation.
- Heart Care – Long-term follow-up for those with heart involvement.
- Rest and Recovery – Patients are advised to rest to minimize stress on the heart and joints.
Prevention of Rheumatic Fever
The best way to prevent is early treatment of strep throat. Here are some key prevention strategies:
- Recognize Symptoms Early – Seek medical care for sore throats, especially in children.
- Complete Antibiotic Courses – Even if symptoms improve, finishing the prescribed antibiotics prevents bacterial survival.
- Maintain Good Hygiene – Frequent handwashing and avoiding sharing personal items can reduce bacterial spread.
- Regular Medical Check-Ups – If you have a history of rheumatic fever, periodic check-ups help prevent complications.
Conclusion
While rheumatic fever is not communicable, the bacterial infection causing it strep throat is highly contagious. Understanding what is rheumatic fever disease, its symptoms, and how to prevent it is crucial for reducing its occurrence.
If you or someone you know experiences frequent sore throats, it’s essential to seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and timely treatment. Early intervention can prevent rheumatic fever and its serious complications, including heart disease. In Ahmedabad, Dr. Dhaiwat Shukla, a leading rheumatologist, specializes in diagnosing and managing rheumatic conditions. Raising awareness and taking prompt medical action can help safeguard your health and ensure a better future.