Introduction:
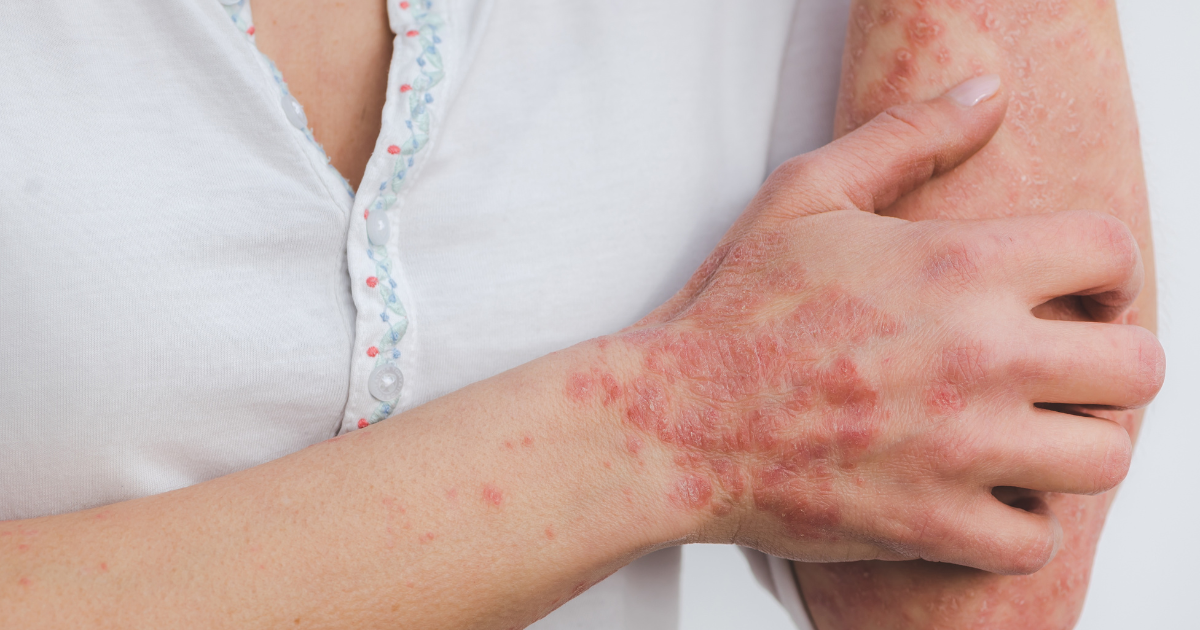
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a complex autoimmune condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by chronic inflammation in the joints, RA can lead to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility, significantly impacting the quality of life for those affected. While medications and therapies are commonly used to manage symptoms and slow disease progression, the role of diet and nutrition in RA management is an increasingly recognized aspect of comprehensive care.
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis:
To effectively manage rheumatoid arthritis, it’s essential to grasp the underlying mechanisms of the disease. In RA, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium, the lining of the joints, leading to inflammation and damage. Genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and hormonal changes are believed to contribute to the development of RA. The chronic inflammation associated with the condition can also affect other organs and systems in the body, leading to complications beyond joint pain.
The Impact of Diet on Rheumatoid Arthritis:
Emerging research suggests that dietary factors may influence the severity of rheumatoid arthritis symptoms and disease progression. While no single diet can cure RA, certain dietary patterns have been associated with improved outcomes and better symptom management. For example, the Mediterranean diet, characterized by high consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and healthy fats like olive oil, has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects and may help reduce joint pain and stiffness in RA patients. On the other hand, diets high in processed foods, saturated fats, and refined sugars have been linked to increased inflammation and disease activity in RA.
Key Nutrients for Rheumatoid Arthritis Management:
Several nutrients play crucial roles in supporting joint health and managing inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis:
Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, as well as in flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts, omega-3s have potent anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce joint pain and inflammation in RA.
Antioxidants: Vitamins C and E, along with selenium, zinc, and carotenoids, act as antioxidants, neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative stress and inflammation in the body.
Vitamin D: Adequate vitamin D levels are essential for bone health and immune function, and low levels of vitamin D have been associated with increased disease activity and joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis.
Calcium: Calcium is vital for maintaining bone density and preventing osteoporosis, a common complication of RA, especially in individuals taking corticosteroids.
Practical Tips for a Rheumatoid Arthritis-Friendly Diet:
Incorporating a rheumatoid arthritis-friendly diet into your lifestyle can be both delicious and beneficial for managing symptoms. Here are some practical tips to help you get started:
Emphasize whole, unprocessed foods: Base your meals around fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to ensure you’re getting a wide range of nutrients that support joint health and overall well-being.
Choose anti-inflammatory fats: Opt for healthy fats like those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, which can help reduce inflammation in the body.
Include fatty fish regularly: Aim to include fatty fish in your diet at least twice a week to increase your intake of omega-3 fatty acids, which are beneficial for RA.
Limit processed foods and sugars: Minimize your consumption of processed foods, sugary snacks, and beverages, as these can contribute to inflammation and exacerbate RA symptoms.
Experiment with herbs and spices: Incorporate anti-inflammatory herbs and spices like turmeric, ginger, cinnamon, and garlic into your cooking to add flavor and boost the nutritional value of your meals.
Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated, as dehydration can worsen joint pain and stiffness.
Conclusion:
Diet and nutrition play a significant role in managing rheumatoid arthritis and supporting overall health and well-being. By making thoughtful dietary choices and adopting healthy eating habits, individuals with RA can complement traditional medical treatments and take an active role in their own care. While there is no one-size-fits-all approach to nutrition for RA, focusing on nutrient-dense, anti-inflammatory foods and consulting with healthcare professionals can help optimize dietary strategies for managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
It’s important to remember that dietary changes alone may not be sufficient to manage RA, and they should be integrated into a comprehensive treatment plan that includes medications, physical activity, and other lifestyle modifications. Working closely with healthcare providers, including rheumatologists and registered dietitians, can help individuals with RA develop personalized dietary strategies that address their unique needs and preferences. With the right guidance and support, adopting a rheumatoid arthritis-friendly diet can be a powerful tool for enhancing overall health and well-being in individuals living with this chronic condition.
Visit Dr. Dhaiwat Shukla, the best Rheumatologist in Ahmedabad known for his compassionate approach to rheumatological care. His expertise, personalized treatment plans, and commitment to improving patients’ well-being make him a trusted choice for those seeking relief from rheumatic conditions.