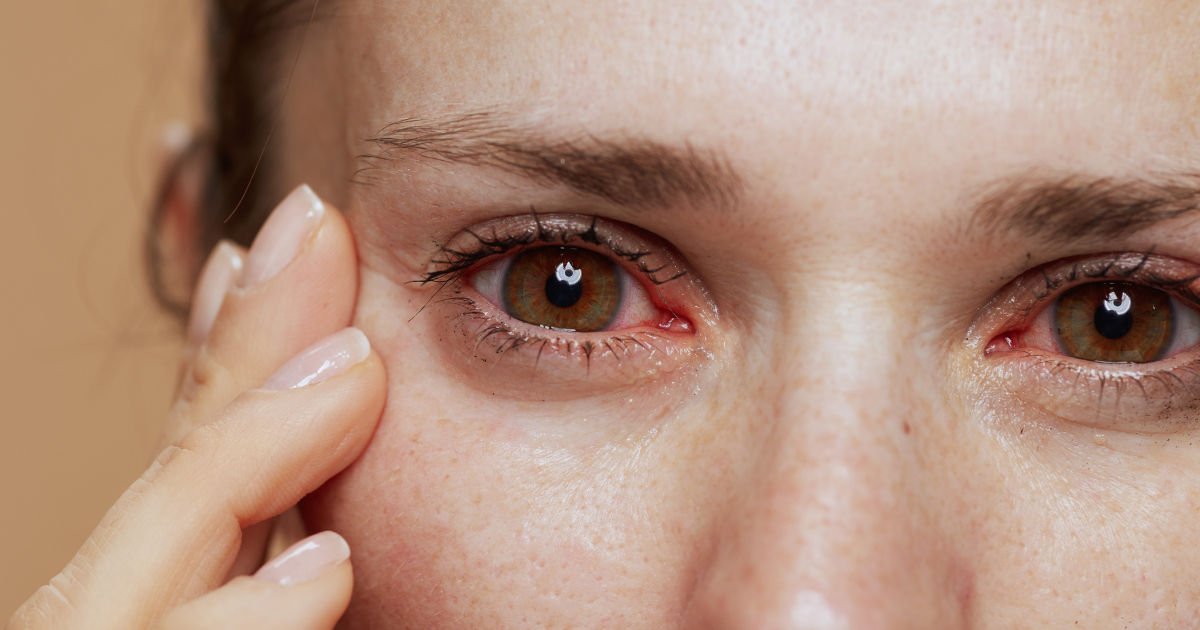
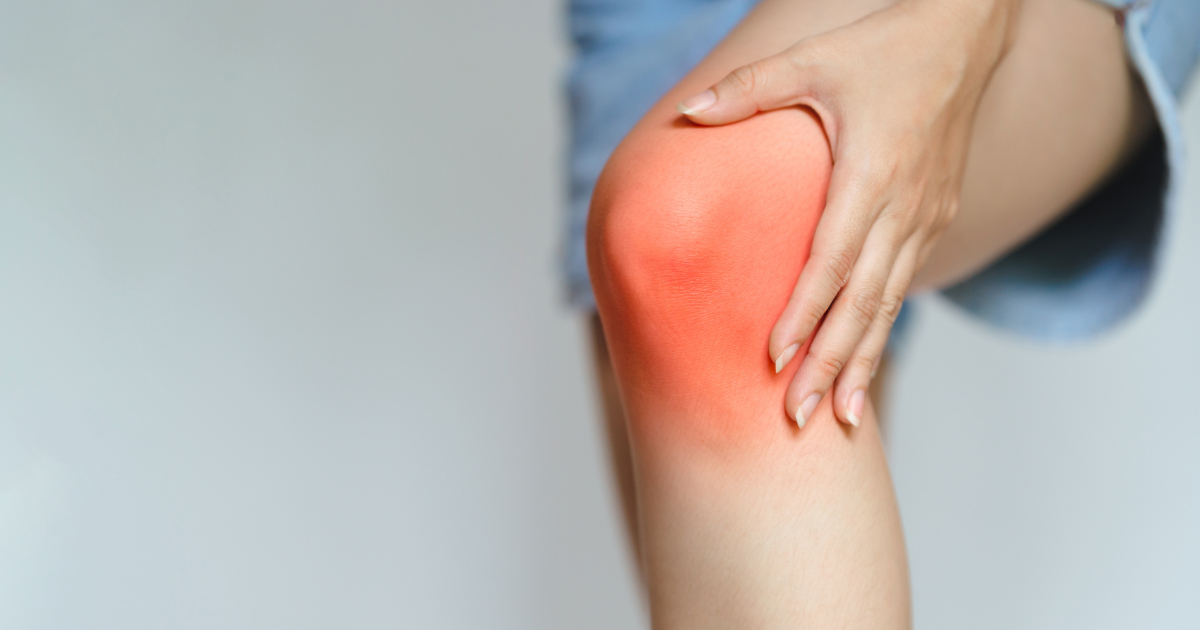
Lupus Erythematosus is a chronic autoimmune disease that disrupts the body’s natural defense mechanisms, causing the immune system to mistakenly attack healthy tissues. This complex condition can affect multiple organs and systems, leading to symptoms ranging from joint pain and skin rashes to severe organ damage. Understanding lupus is crucial for early detection and effective management, as timely interventions can significantly improve a patient’s quality of life.
This blog delves into the essentials of lupus, exploring its causes, symptoms, and effective strategies for managing the disease. Whether you or a loved one are living with lupus or seeking to understand its impact, this guide provides insights and practical advice to navigate life with this challenging condition.
What is Lupus Erythematosus?
Lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune disease that causes the immune system to become hyperactive and attack healthy tissues. The body’s immune system, which typically defends against infections, begins to attack the body’s own cells and tissues. This leads to widespread inflammation and damage to affected organs. There are different types of lupus, but Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is the most common, affecting multiple parts of the body. Other forms of lupus include Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE), which mainly affects the skin, and Drug-induced Lupus, triggered by certain medications.
Types of Lupus:
Lupus Erythematosus is classified into several types based on its symptoms, affected organs, and severity. The most common types include
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): This is the most common type and can affect various organs, including the kidneys, heart, lungs, and brain. It is often diagnosed by a combination of symptoms, blood tests, and imaging.
- Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE): This type is primarily limited to the skin and causes scarring rashes, most commonly on the face, scalp, and ears.
- Drug-induced Lupus: This form of lupus is triggered by certain medications, with symptoms similar to SLE, but it is reversible once the medication is stopped.
- Neonatal Lupus: A rare form of lupus that affects infants born to mothers who have lupus. The symptoms usually resolve after birth but can cause skin rashes or heart problems in newborns.
- Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (SCLE): A milder form of lupus that primarily affects the skin, causing red, scaly patches or lesions. It is often triggered by sun exposure.
Symptoms of Lupus Erythematosus:
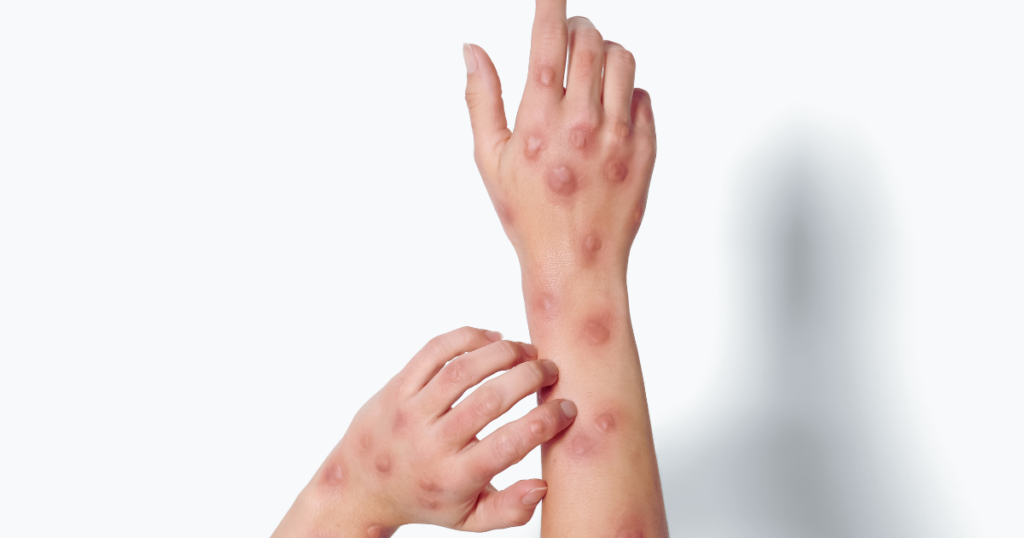
Lupus presents in different ways for each person, but some common symptoms include:
- Fatigue: Chronic tiredness is one of the most common and debilitating symptoms of lupus.
- Joint Pain and Swelling: Lupus can cause arthritis-like symptoms, often affecting small joints such as those in the hands, wrists, and knees.
- Skin Rash: A butterfly-shaped rash that appears across the cheeks and nose is a hallmark sign of lupus, especially in SLE.
- Sun Sensitivity: Many lupus patients are sensitive to sunlight, which can trigger rashes and flare-ups.
- Kidney Problems: Lupus nephritis occurs when lupus affects the kidneys, leading to kidney inflammation and potential kidney failure if untreated.
- Chest Pain and Breathing Issues: Lupus can cause inflammation of the heart or lungs, leading to chest pain and difficulty breathing.
- Neurological Symptoms: Some lupus patients may experience headaches, dizziness, seizures, or even memory problems due to lupus affecting the nervous system.
Diagnosing Lupus Erythematosus :
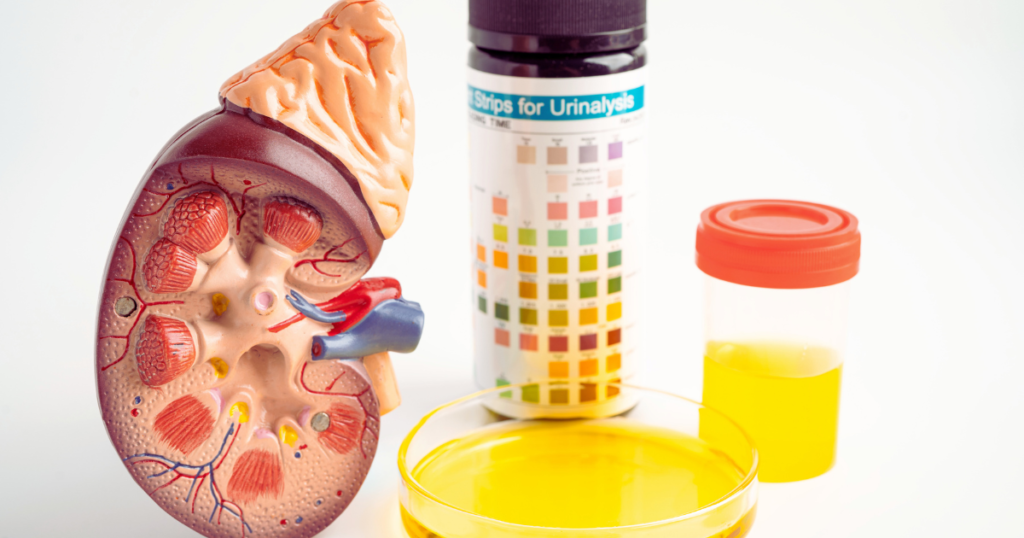
Diagnosing lupus is a complex process because its symptoms overlap with many other diseases. A thorough diagnosis requires a combination of clinical evaluations and laboratory tests. Some common diagnostic methods include:
- Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) Test: This test looks for antibodies that attack the body’s own cells, which are often found in lupus patients.
- Blood Tests: These tests check for signs of inflammation and the presence of specific antibodies associated with lupus.
- Urinalysis: Kidney involvement is common in lupus, and urinalysis helps detect kidney damage by checking for protein or blood in the urine.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays or CT scans can be used to check for lung or heart involvement.
- Biopsy: In cases of kidney or skin involvement, a biopsy may be performed to determine the extent of the damage.
The Impact of Lupus Erythematosus on Daily Life
Lupus can be a chronic and debilitating condition that impacts many aspects of life. Because the disease affects multiple organs, it can cause physical, emotional, and mental distress. Managing lupus requires constant monitoring, medication, and lifestyle adjustments. Patients with lupus may experience flare-ups, during which symptoms worsen, and remissions, where symptoms improve or disappear. Some of the challenges of living with lupus include:
- Managing Flare-Ups: Flare-ups can vary in severity, and managing them effectively is crucial to preventing organ damage.
- Emotional Health: Dealing with a chronic condition like lupus can be emotionally draining. Depression and anxiety are common among people with lupus.
- Physical Limitations: Chronic pain and fatigue can make it difficult to perform daily tasks, affecting quality of life.
- Work and Social Life: The unpredictable nature of lupus can interfere with work, relationships, and social activities, as flare-ups may cause patients to miss work or social events.
Treatment and Management of Lupus :

While there is no cure for lupus, effective treatments are available to manage symptoms and prevent complications. Treatment plans are highly individualized based on the severity of the disease, organs involved, and patient response. Common treatment strategies include:
- Medications:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): These drugs help reduce pain and inflammation in the joints.
- Antimalarial Drugs (e.g., Hydroxychloroquine): These drugs are commonly used in lupus treatment and help control symptoms like rashes and joint pain.
- Corticosteroids: These are used to reduce inflammation, especially during flare-ups.
- Immunosuppressive Drugs: In severe cases, drugs that suppress the immune system, like methotrexate or cyclophosphamide, may be prescribed to prevent organ damage.
- Biologics: Newer drugs such as belimumab are designed to target specific parts of the immune system and reduce disease activity.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Sun Protection: Sun exposure can trigger flare-ups, so wearing sunscreen, protective clothing, and avoiding peak sunlight hours is essential.
- Dietary Changes: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce inflammation. Foods high in antioxidants can protect against joint damage.
- Exercise: Low-impact activities like swimming, walking, and yoga can help improve mobility and reduce joint stiffness.
- Stress Management: Practicing relaxation techniques like meditation, deep breathing, and mindfulness can help manage stress, which is known to trigger flare-ups.
- Regular Monitoring and Check-Ups:
- Lupus patients need regular visits to their rheumatologist for check-ups and monitoring of organ function, particularly kidney and cardiovascular health.
Living with Lupus Erythematosus: A Path to Empowerment
Although lupus is a chronic disease, many people live fulfilling lives by effectively managing their symptoms and making lifestyle changes. Early diagnosis, proper treatment, and ongoing care are essential for preventing complications and improving quality of life. With support from healthcare professionals, loved ones, and support groups, individuals with lupus can lead active, healthy lives despite the challenges posed by the disease.
FAQs:
- What is lupus erythematosus?
Lupus erythematosus is a chronic autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks healthy tissues, causing inflammation and damage to various organs. - What are common symptoms of lupus?
Symptoms include fatigue, joint pain, skin rashes, fever, and organ-related issues such as kidney inflammation or heart complications. - How is lupus diagnosed?
Lupus is diagnosed through a combination of physical exams, blood tests (like ANA), and imaging studies to assess organ involvement. - Is lupus curable?
There is no cure for lupus, but treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent flares. - What triggers lupus flares?
Common triggers include stress, sunlight exposure, infections, and certain medications. - What are effective treatments for lupus?
Treatments include anti-inflammatory medications, immunosuppressants, corticosteroids, and lifestyle changes to reduce inflammation and manage symptoms. - Can diet help manage lupus?
Yes, an anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, omega-3 fatty acids, and whole grains can support overall health. - How does lupus affect daily life?
Lupus can cause fatigue and joint pain, making routine tasks challenging, but proper treatment and self-care can improve quality of life. - Is lupus hereditary?
While lupus isn’t directly inherited, genetic factors can increase the risk, especially in families with a history of autoimmune diseases. - Can lupus lead to complications?
Yes, complications can include kidney damage, cardiovascular issues, and lung inflammation, among others. - How can I prevent lupus flares?
Prevent flares by avoiding triggers, following your treatment plan, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. - What is lupus nephritis?
Lupus nephritis is a serious complication where lupus causes inflammation in the kidneys, affecting their function. - Who is at higher risk for lupus?
Lupus is more common in women, particularly those of childbearing age, and is more prevalent in certain ethnic groups. - Can lupus affect pregnancy?
Yes, lupus can affect pregnancy, but with proper management, many women with lupus can have healthy pregnancies. - When should I see a rheumatologist for lupus?
If you experience unexplained fatigue, joint pain, or persistent rashes, consult a rheumatologist for proper evaluation and treatment. - Where can I find the best rheumatologists in Ahmedabad for lupus treatment?
In Ahmedabad, you can consult rheumatologists at top healthcare facilities like Dr. Dhaiwat Shukla’s Clinic specialize in autoimmune diseases like lupus.
Call to action :
Autoimmune disease lupus erythematosus, while complex, is manageable with early diagnosis, a tailored treatment plan, and lifestyle adjustments. Patients with lupus need to work closely with healthcare providers to develop an effective management strategy. With proper care and attention, those living with lupus can achieve symptom relief, prevent flare-ups, and lead meaningful lives. If you suspect you may have lupus or are experiencing symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.