Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes inflammation and damage to the joints. While its primary impact is on the joints, it can also lead to other complications outside the joints, including the formation of rheumatoid nodules. These nodules are one of the most common extra-articular (outside of the joints) manifestations of RA, and they affect a significant number of individuals with this disease.
In this comprehensive blog, we will explore what rheumatoid nodules are, their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. We will also discuss the relationship between nodules from RA and how they fit into the overall management RA.
What Are Rheumatoid Nodules:
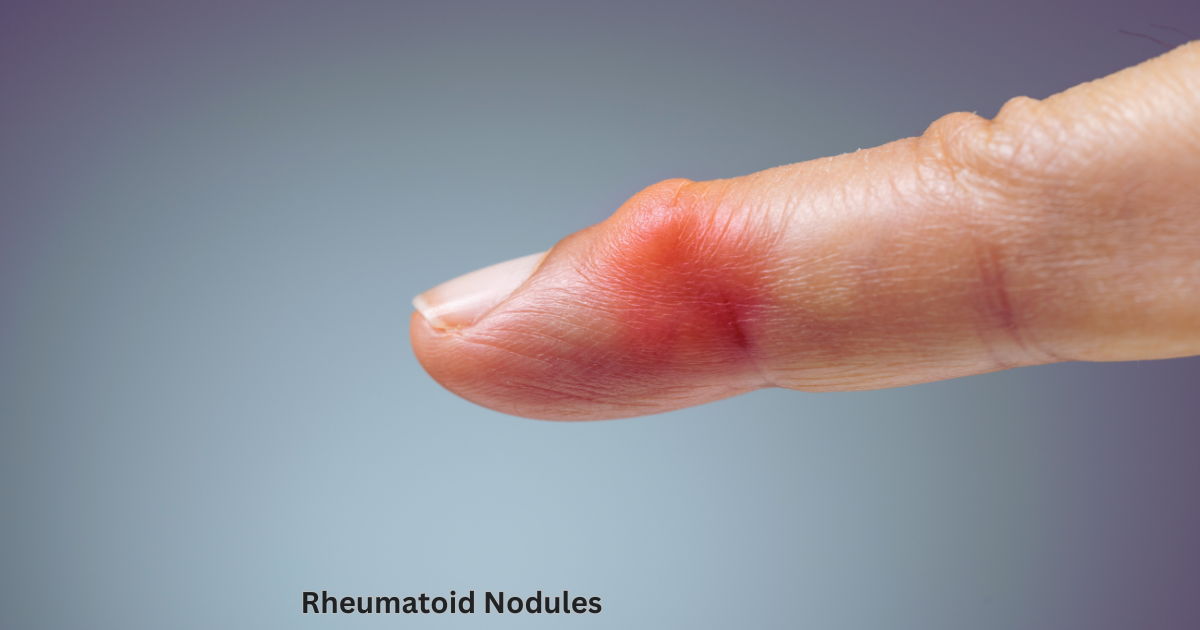
Rheumatoid nodules are firm, non-tender lumps that develop under the skin, typically over bony prominences such as the elbows, fingers, and forearms. They are a type of subcutaneous nodule, meaning they form under the skin layer. These nodules are most commonly seen in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis, particularly in those with more severe or long-standing disease.
While these nodules are associated with RA, not all individuals with RA will develop them. The presence of nodules can indicate a more aggressive form of the disease and may be linked to higher levels of rheumatoid factor (RF) in the blood. However, nodules are not harmful in themselves and do not usually affect the function of the joints directly, though they can cause discomfort if they become infected or grow large.
Understanding the Causes :
The exact cause of nodules is not completely understood, but several factors have been identified that contribute to their development:
- Autoimmune Reaction:
- RA is an autoimmune disease, where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own healthy tissues, particularly the joints. The same immune system malfunction can lead to the formation of nodules.
- High Levels of Rheumatoid Factor:
- Individuals with higher levels of rheumatoid factor (RF), a protein produced by the immune system, are more likely to develop nodules. Elevated RF levels are often seen in people with more severe RA.
- Genetic Factors:
- Genetic factors can influence a person’s susceptibility to both rheumatoid arthritis and the formation of nodules. People with certain genetic markers are at an increased risk of developing nodules.
- Smoking:
- Smoking is a well-established risk factor for the development of rheumatoid nodules. Smokers with RA are more likely to experience nodules than non-smokers.
- Duration and Severity of RA:
- Longer-standing and more severe cases of RA tend to be associated with the development of rheumatoid nodules. The more active and untreated the disease, the higher the likelihood of nodules forming.
Identifying Symptoms :
There are often asymptomatic (without symptoms), but in some cases, they can cause discomfort or even interfere with daily activities. Common symptoms and characteristics of rheumatoid nodules include:
- Firm Lumps Under the Skin:
- Nodules are typically round, hard, and firm to the touch. They are most commonly found on the elbows, forearms, fingers, and occasionally on the scalp, lungs, and internal organs.
- Painless or Tender:
- In most cases, rheumatoid nodules are painless. However, some individuals may experience tenderness, especially if the nodules are located near nerve endings or joints.
- Size and Growth:
- Nodules can vary in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter. They may grow over time or remain stable in size.
- Infection and Inflammation:
- If a nodule becomes infected, it may become red, swollen, and painful. In such cases, the skin over the nodule may break open, leading to an open wound or abscess.
The Process of Diagnosing :
The diagnosis of nodules is typically straightforward, as they are visible under the skin and can be felt during a physical examination. However, there are several steps involved in confirming the presence of these nodules:
- Physical Examination:
- A doctor will examine the skin for the characteristic lumps of rheumatoid nodules. The doctor will also evaluate the location and firmness of the nodules.
- Medical History:
- The doctor will review the patient’s medical history to assess whether they have a known diagnosis of arthritis or if they exhibit symptoms consistent with RA.
- Rheumatoid Factor Test:
- Elevated levels of rheumatoid factor (RF) in the blood may indicate RA and an increased likelihood of developing nodules. However, some individuals with RA may not have elevated RF levels.
- Biopsy:
- In rare cases, a small tissue sample (biopsy) may be taken from the nodule to rule out other conditions, such as infections or cancer.
- Imaging Tests:
- While imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI are not typically used to diagnose nodules, they may be useful in assessing the surrounding tissue or joint involvement if necessary.
Managing Treatment :
Although rheumatoid nodules are generally not dangerous, their management may be necessary if they cause discomfort or complications. Several treatment options are available, depending on the severity of the nodules and their impact on the patient’s quality of life.
- Medication for RA:
- Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): Medications like methotrexate and hydroxychloroquine help control the underlying RA, potentially reducing the formation of new nodules.
- Biologics: Drugs such as tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNF inhibitors) target specific aspects of the immune system to control inflammation and reduce nodules.
- Corticosteroids: Oral or injected steroids can help reduce inflammation and may shrink nodules in some cases.
- Steroid Injections:
- If the nodules are causing pain or inflammation, corticosteroid injections may help reduce swelling and discomfort. These injections may also help prevent the formation of new nodules.
- Surgical Removal:
- In rare cases where nodules are large, painful, or infected, surgery may be required to remove them. This is generally reserved for nodules that are causing significant problems.
- Smoking Cessation:
- Quitting smoking can help reduce the risk of developing nodules and may prevent existing nodules from worsening. Smoking cessation is an important part of managing rheumatoid arthritis.
Prevention of Rheumatoid Nodules
While it may not be possible to prevent nodules entirely, certain measures can reduce the likelihood of their development:
- Early and Effective RA Treatment:
- Prompt diagnosis and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with disease-modifying drugs (DMARDs) can help control inflammation and reduce the risk of developing nodules.
- Smoking Cessation:
- As smoking is a significant risk factor for nodules, quitting smoking can help lower the risk of developing the nodules and improve overall RA management.
- Regular Monitoring:
Regular check-ups with a rheumatologist can help monitor RA progression and address the development of nodules early.
FAQ:
- What are rheumatoid nodules?
This nodules are firm lumps that develop under the skin near joints in some people with rheumatoid arthritis. They are a common extra-articular manifestation of RA. - Are rheumatoid nodules a sign of severe RA?
Yes, they are often associated with more severe or advanced rheumatoid arthritis and can indicate active disease. - What do rheumatoid nodules look like?
They are usually round, firm, and painless lumps found under the skin, often near joints like elbows, fingers, or the forearm. - Can rheumatoid nodules be painful?
Most nodules are painless, but they can become tender or sore if they press on nerves or if there’s inflammation around them. - How are rheumatoid nodules diagnosed?
Diagnosis is typically based on physical examination and medical history. In some cases, a biopsy may be done to confirm the diagnosis. - Do rheumatoid nodules require treatment?
Treatment isn’t always necessary unless the nodules are causing discomfort, restricting movement, or becoming infected. - Can lifestyle changes help reduce rheumatoid nodules?
While lifestyle changes won’t remove nodules, managing overall RA symptoms through a healthy diet, exercise, and stress management may help reduce their progression. - Can rheumatoid nodules affect joint function?
If the nodules are large or located near tendons and nerves, they may limit movement or cause discomfort during daily activities. - How can caregivers support someone with rheumatoid nodules?
Encourage the patient to follow their treatment plan, attend regular rheumatologist appointments, and maintain a supportive and understanding environment. - Should families worry if nodules appear?
Rheumatoid nodules may indicate active RA but aren’t life-threatening. Consult Dr. Dhaiwat Shukla for proper management and treatment. - Who is at risk of developing rheumatoid nodules?
People with advanced RA, high levels of rheumatoid factor (RF), or who smoke are at higher risk of developing nodules. - Can stopping smoking help with nodules?
Yes, quitting smoking can reduce the severity of RA and may prevent further nodules from forming. - Can rheumatoid nodules recur after removal?
Yes, nodules can recur, especially if the underlying RA is not well-controlled. - Do rheumatoid nodules appear suddenly?
They usually develop gradually over time as RA progresses, but in some cases, they can appear more quickly during disease flare-ups. - What should I do if my nodule becomes infected?
Seek medical attention immediately. Infections may require antibiotics or drainage procedures.
Conclusion
Rheumatoid nodules are a common extra-articular manifestation of rheumatoid arthritis, typically seen in individuals with more severe or long-standing disease. While these nodules are often harmless, they can cause discomfort and may indicate a need for better disease management. Effective treatment of RA with medications, lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, and regular monitoring can help manage rheumatoid nodules and reduce their impact on the patient’s health.
If you are living with rheumatoid arthritis and are concerned about the development of rheumatoid nodules, consulting with a rheumatologist like Dr. Dhaiwat Shukla, one of the best rheumatologists in Ahmedabad, can help you understand the condition better and guide you toward the most effective treatment options.