Scleroderma, an enigmatic chronic autoimmune disorder, poses a myriad of challenges for those affected. From its subtle onset to potentially severe complications, understanding this condition is paramount. Let’s delve into the intricate web exploring its causes, symptoms, diverse treatment options, and strategies for living with the condition.
What is Scleroderma?
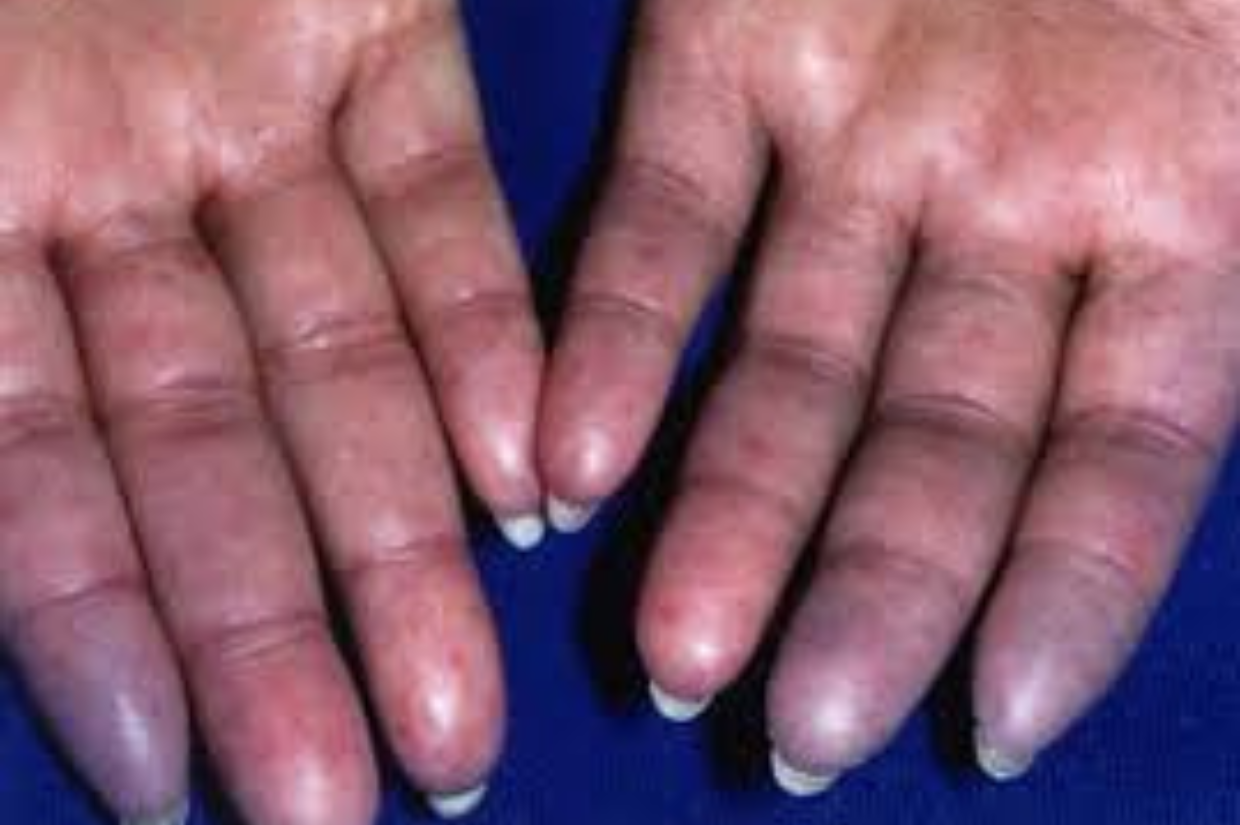
Scleroderma, derived from Greek words meaning “hard skin,” manifests as an abnormal growth of connective tissue. While it predominantly affects the skin, it can extend its grasp to internal organs, blood vessels, and the digestive tract. This condition arises from the immune system erroneously attacking healthy tissues, leading to inflammation and excessive collagen production.
Causes-
The precise etiology of scleroderma remains elusive, yet several factors are believed to contribute to its development. Genetic predispositions, environmental triggers, and an overactive immune response are thought to play significant roles. Triggers such as infections, exposure to certain chemicals, and hormonal imbalances have been implicated in initiating the disease process.
Symptoms-
Scleroderma can manifest in various forms, each presenting its unique set of symptoms. Common manifestations include:
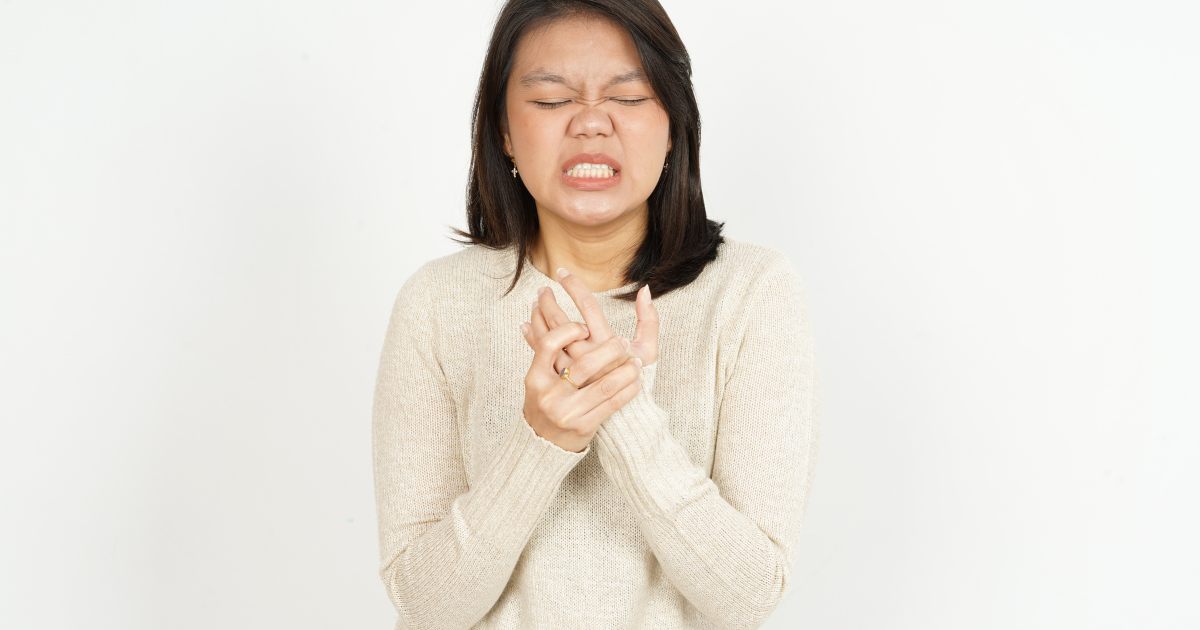
- Skin Changes: Thickening and hardening of the skin, particularly on the fingers, hands, face, and trunk.
- Raynaud’s Phenomenon: Characterized by changes in skin color due to reduced blood flow, especially in response to cold temperatures or stress.
- Digestive Issues: Acid reflux, difficulty swallowing, bloating, and malabsorption due to gastrointestinal involvement.
- Joint Pain: Inflammation and stiffness in the joints, resembling symptoms of arthritis.
- Organ Involvement: Complications may arise if internal organs such as the lungs, heart, kidneys, or esophagus are affected.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing scleroderma often involves a combination of clinical assessment, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Treatment strategies aim to manage symptoms, prevent complications, and improve quality of life. These may include:
- Medications: Immunosuppressants, anti-inflammatory drugs, and medications to manage specific symptoms like Raynaud’s phenomenon.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to maintain joint flexibility, improve circulation, and prevent muscle atrophy.
- Skin Care: Moisturizers and gentle skincare routines to alleviate dryness and prevent skin complications.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical interventions such as joint replacement or lung transplantation may be necessary.
Living with Scleroderma
Coping with scleroderma requires a multifaceted approach and ongoing support. Patients, along with their caregivers, find solace in understanding the condition and adapting to its challenges. Here are additional insights into living with scleroderma:
- Psychological Impact: Scleroderma’s physical manifestations often extend to psychological ramifications. Patients may experience anxiety, depression, or feelings of isolation due to the chronic nature of the disease and its unpredictable course. Mental health support and counseling play a crucial role in addressing these emotional challenges.
- Social Support Networks: Engaging with support groups and connecting with individuals facing similar challenges can provide invaluable support and camaraderie. Sharing experiences, tips for managing symptoms, and coping strategies within these communities foster a sense of belonging and empowerment.
- Fatigue Management: Chronic fatigue is a common symptom of scleroderma and can significantly impact daily functioning. Learning to pace oneself, prioritize tasks, and incorporate rest breaks throughout the day can help manage fatigue levels and conserve energy.
- Diet and Nutrition: While there is no specific diet for scleroderma, adopting a balanced and nutritious diet can support overall health and well-being. Some individuals find that certain foods or dietary supplements alleviate symptoms or improve digestion. Consulting with a registered dietitian can provide personalized dietary recommendations.
- Monitoring and Follow-Up Care: Regular monitoring by healthcare professionals is essential for assessing disease progression, monitoring organ involvement, and adjusting treatment as needed. Patients should maintain open communication with their healthcare team, reporting any new or worsening symptoms promptly.
- Advocacy and Awareness: Increasing awareness about scleroderma within the broader community can help dispel misconceptions and facilitate early diagnosis. Patient advocacy efforts, participation in awareness campaigns, and fundraising initiatives contribute to advancing research and improving patient care.
- Research and Clinical Trials: Participating in clinical trials and research studies offers patients an opportunity to contribute to the advancement of scleroderma knowledge and treatment options. It also provides access to cutting-edge therapies and specialized care under the guidance of experienced researchers and clinicians.
In conclusion, navigating life with scleroderma requires resilience, adaptability, and a supportive network of healthcare professionals, caregivers, and peers. By embracing a holistic approach to management, individuals with scleroderma can strive for improved quality of life and a sense of empowerment in their journey.
In essence, while scleroderma may test one’s endurance, it also highlights the resilience of the human spirit in overcoming adversity. Let knowledge be the beacon guiding us toward better understanding, management, and ultimately, triumph over this enigmatic autoimmune disorder.
Visit Dr. Dhaiwat Shukla, the best Rheumatologist in Ahmedabad known for his compassionate approach to rheumatological care. His expertise, personalized treatment plans, and commitment to improving patients’ well-being make him a trusted choice for those seeking relief from rheumatic conditions.